异步任务队列¶
异步任务使您能够以“即发即弃”的方式处理某些推理任务。您无需等待响应,而是可以提交一个在后台运行的请求,并立即收到一个唯一标识符。然后,可以在任何时候使用此标识符来检查任务状态或在任务完成后检索结果。这使得在不需要立即结果的场景中,能够更有效地利用资源并提高响应能力。
异步任务非常适合
批量处理:对大量数据运行推理
异步生成:生成文本、图像或其他可能需要很长时间才能完成的媒体
对时间不敏感的任务:不需要立即完成,可以以较低优先级执行的任务
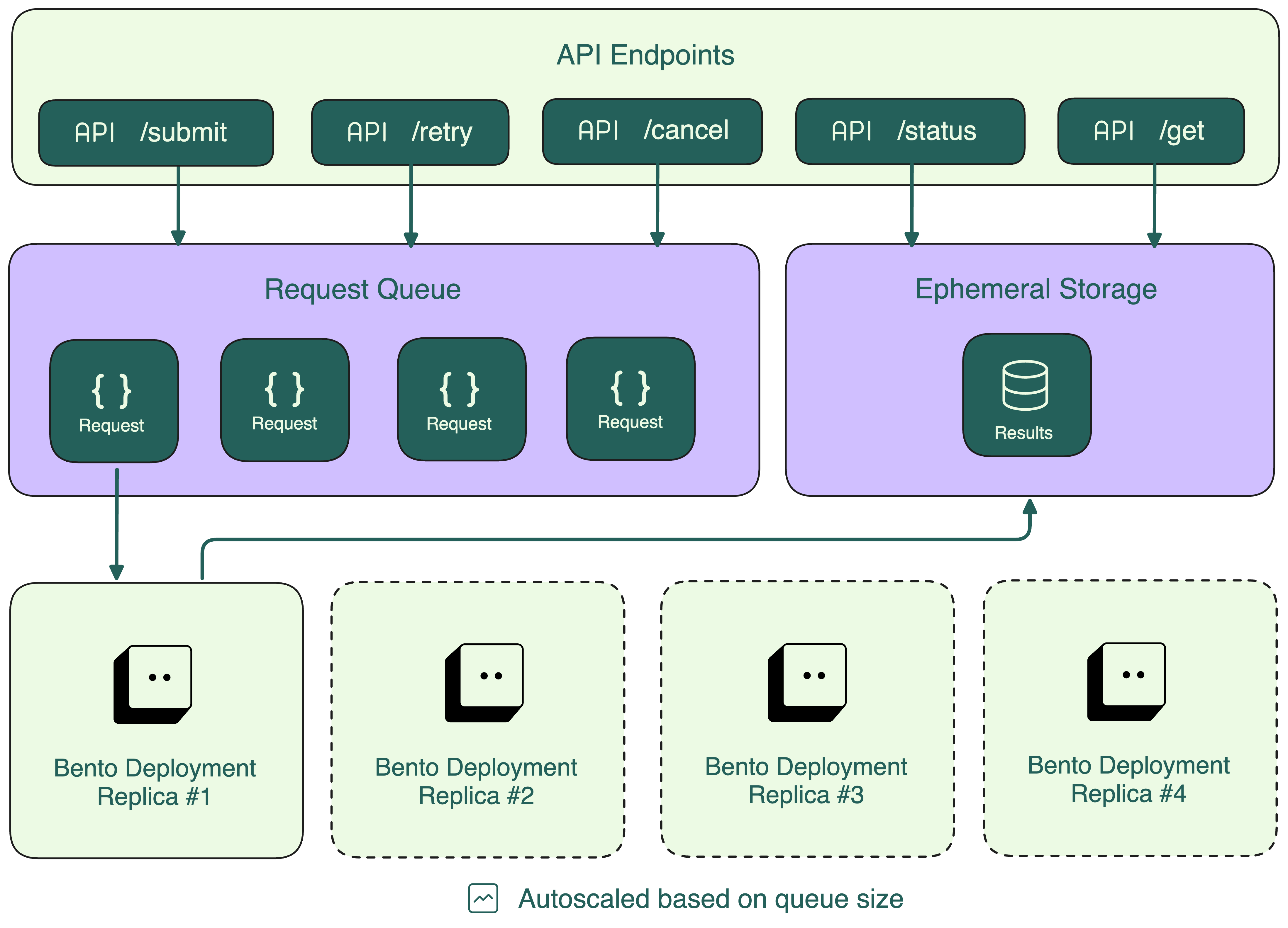
任务结果会存储一段可配置的时间,默认为 24 小时,之后将被删除。
注意
上图展示了在 BentoCloud 上运行异步任务的架构。当 BentoML 服务在本地部署时,请求队列和临时存储是在非持久性内存中创建的,仅用于开发目的。
定义任务端点¶
您可以在 Service 构造函数中使用 @bentoml.task 装饰器来定义任务端点。如果您已经有一个 @bentoml.api 并想将其转换为异步任务,您只需更改装饰器即可,无需修改函数实现。以下是一个示例
import bentoml
from PIL.Image import Image
@bentoml.service
class ImageGenerationService:
@bentoml.task
def long_running_image_generation(self, prompt: str) -> Image:
# Process the prompt in a long-running process
return image
在底层,BentoML 自动生成多个端点,用于创建任务、获取任务状态和检索任务结果。
POST /submit: 提交任务到队列。立即返回一个唯一的任务标识符。GET /status: 根据任务标识符获取任务状态。GET /get: 根据任务标识符获取任务结果。POST /cancel: 根据任务标识符尝试取消任务,如果任务尚未开始执行。PUT /retry: 根据任务标识符重试任务。
调用任务端点¶
可以通过 SyncHTTPClient 或 AsyncHTTPClient 客户端提交异步任务,使用端点名称上的 submit() 函数。
import bentoml
prompt = "a scenic mountain view that ..."
client = bentoml.SyncHTTPClient('https://:3000')
# The arguments are the same as the Service method, just call with `.submit()`
task = client.long_running_image_generation.submit(prompt=prompt)
print("Task submitted, ID:", task.id)
注意
您也可以使用任何语言的 HTTP 客户端直接调用上面列出的端点。
任务提交后,请求会排队到请求队列中,并立即返回一个唯一的任务标识符,该标识符可用于获取状态和检索结果。
# Use the following code at a later time
status = task.get_status()
if status.value == 'success':
print("The task runs successfully. The result is", task.get())
elif status.value == 'failure':
print("The task run failed.")
else:
print("The task is still running.")
如果任务失败或您需要使用相同的参数重新运行任务,请使用 retry()。
status = task.get_status()
if status.value == 'failure':
print("Task failed, retrying...")
new_task = task.retry()
new_status = new_task.get_status()
print("New task status:", new_status.value)
更多信息请参阅调用 API 端点。