模型组合¶
模型组合允许您结合多个模型来构建复杂的 AI 应用,例如 RAG 和 AI Agent。BentoML 提供了简单的服务 API,用于创建模型需要协同工作(按顺序或并行)的工作流。
您可能需要在以下情况下使用 BentoML 中的模型组合:
使用不同的模型一起处理不同类型的数据(例如,图像和文本)
通过组合多个模型的结果来提高准确性和性能
在专用硬件(例如,GPU 和 CPU)上运行不同的模型
使用专用模型或服务编排序列步骤,如预处理、推理和后处理
另请参见
更多信息,请参阅博客文章 A Guide to Model Composition。
示例¶
BentoML 中的模型组合可以涉及单个或多个服务,具体取决于您的应用。
对于每个服务,您可以在 @bentoml.service 装饰器中使用 resources 来配置部署所需的资源,例如 GPU。请注意,此字段仅在 BentoCloud 上生效。
在一个服务中运行多个模型¶
您可以在同一硬件设备上运行多个模型,并为它们公开单独或组合的 API。
import bentoml
from bentoml.models import HuggingFaceModel
from transformers import pipeline
from typing import List
# Run two models in the same Service on the same hardware device
@bentoml.service(
resources={"gpu": 1, "memory": "4GiB"},
traffic={"timeout": 20},
)
class MultiModelService:
# Retrieve model references from HF by specifying its HF ID
model_a_path = HuggingFaceModel("FacebookAI/roberta-large-mnli")
model_b_path = HuggingFaceModel("distilbert/distilbert-base-uncased")
def __init__(self) -> None:
# Initialize pipelines for each model
self.pipeline_a = pipeline(task="zero-shot-classification", model=self.model_a_path, hypothesis_template="This text is about {}")
self.pipeline_b = pipeline(task="sentiment-analysis", model=self.model_b_path)
# Define an API for data processing with model A
@bentoml.api
def process_a(self, input_data: str, labels: List[str] = ["positive", "negative", "neutral"]) -> dict:
return self.pipeline_a(input_data, labels)
# Define an API for data processing with model B
@bentoml.api
def process_b(self, input_data: str) -> dict:
return self.pipeline_b(input_data)[0]
# Define an API endpoint that combines the processing of both models
@bentoml.api
def combined_process(self, input_data: str, labels: List[str] = ["positive", "negative", "neutral"]) -> dict:
classification = self.pipeline_a(input_data, labels)
sentiment = self.pipeline_b(input_data)[0]
return {
"classification": classification,
"sentiment": sentiment
}
注意
HuggingFaceModel 函数以字符串形式返回下载的模型路径。您必须传入 Hugging Face 上显示的模型 ID(例如,HuggingFaceModel("FacebookAI/roberta-large-mnli"))。详情请参阅加载和管理模型。
在单独的服务中独立运行和扩展多个模型¶
当您的模型需要独立扩展或不同的硬件时,将它们拆分为单独的服务。
顺序执行¶
您可以让模型按顺序工作,其中一个模型的输出成为另一个模型的输入。这对于创建需要先对数据进行预处理再用于预测的流水线非常有用。
import bentoml
from bentoml.models import HuggingFaceModel
from transformers import pipeline
from typing import Dict, Any
@bentoml.service(resources={"cpu": "2", "memory": "2Gi"})
class PreprocessingService:
model_a_path = HuggingFaceModel("distilbert/distilbert-base-uncased")
def __init__(self) -> None:
# Initialize pipeline for model A
self.pipeline_a = pipeline(task="text-classification", model=self.model_a_path)
@bentoml.api
def preprocess(self, input_data: str) -> Dict[str, Any]:
# Dummy preprocessing steps
return self.pipeline_a(input_data)[0]
@bentoml.service(resources={"gpu": 1, "memory": "4Gi"})
class InferenceService:
model_b_path = HuggingFaceModel("distilbert/distilroberta-base")
preprocessing_service = bentoml.depends(PreprocessingService)
def __init__(self) -> None:
# Initialize pipeline for model B
self.pipeline_b = pipeline(task="text-classification", model=self.model_b_path)
@bentoml.api
async def predict(self, input_data: str) -> Dict[str, Any]:
# Dummy inference on preprocessed data
# Implement your custom logic here
preprocessed_data = await self.preprocessing_service.to_async.preprocess(input_data)
final_result = self.pipeline_b(input_data)[0]
return {
"preprocessing_result": preprocessed_data,
"final_result": final_result
}
您可以使用 bentoml.depends 从一个服务访问另一个服务。它接受依赖的服务类作为参数,并允许您调用其可用的函数。详情请参阅运行分布式服务。
您可以使用服务的 .to_async 属性将同步方法转换为异步。请注意,不建议在异步上下文中直接调用同步阻塞函数,因为它可能会阻塞事件循环。
并行执行¶
您可以同时运行多个独立模型,然后组合它们的结果。这对于集成模型非常有用,您可以在其中聚合来自不同模型的预测结果以提高准确性。
import asyncio
import bentoml
from bentoml.models import HuggingFaceModel
from transformers import pipeline
from typing import Dict, Any, List
@bentoml.service(resources={"gpu": 1, "memory": "4Gi"})
class ModelAService:
model_a_path = HuggingFaceModel("FacebookAI/roberta-large-mnli")
def __init__(self) -> None:
# Initialize pipeline for model A
self.pipeline_a = pipeline(task="zero-shot-classification", model=self.model_a_path, hypothesis_template="This text is about {}")
@bentoml.api
def predict(self, input_data: str, labels: List[str] = ["positive", "negative", "neutral"]) -> Dict[str, Any]:
# Dummy preprocessing steps
return self.pipeline_a(input_data, labels)
@bentoml.service(resources={"gpu": 1, "memory": "4Gi"})
class ModelBService:
model_b_path = HuggingFaceModel("distilbert/distilbert-base-uncased")
def __init__(self) -> None:
# Initialize pipeline for model B
self.pipeline_b = pipeline(task="sentiment-analysis", model=self.model_b_path)
@bentoml.api
def predict(self, input_data: str) -> Dict[str, Any]:
# Dummy preprocessing steps
return self.pipeline_b(input_data)[0]
@bentoml.service(resources={"cpu": "4", "memory": "8Gi"})
class EnsembleService:
service_a = bentoml.depends(ModelAService)
service_b = bentoml.depends(ModelBService)
@bentoml.api
async def ensemble_predict(self, input_data: str, labels: List[str] = ["positive", "negative", "neutral"]) -> Dict[str, Any]:
result_a, result_b = await asyncio.gather(
self.service_a.to_async.predict(input_data, labels),
self.service_b.to_async.predict(input_data)
)
# Dummy aggregation
return {
"zero_shot_classification": result_a,
"sentiment_analysis": result_b
}
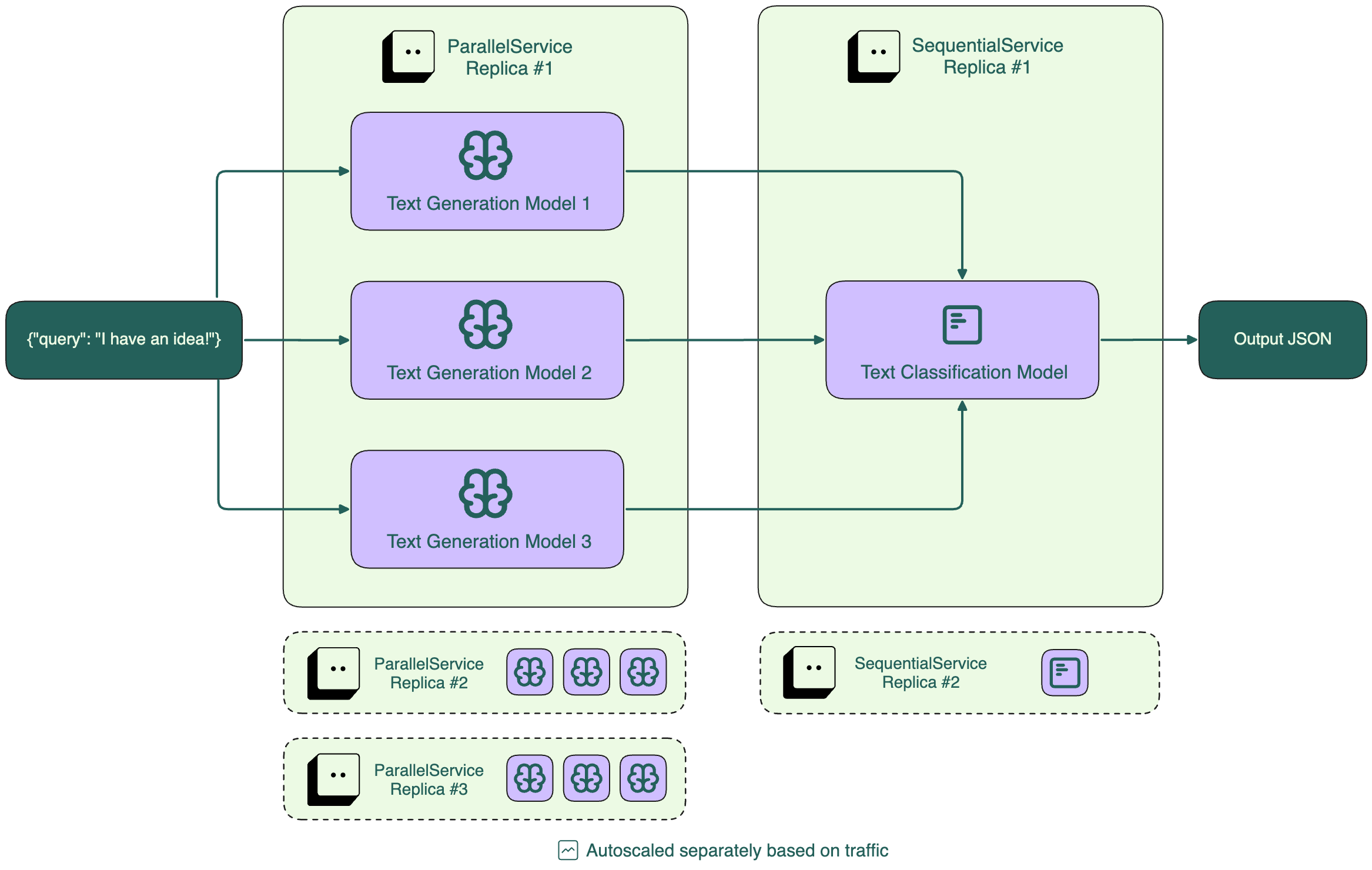
推理图¶
您可以创建结合并行和顺序处理的更复杂工作流。
import asyncio
import typing as t
import transformers
import bentoml
MAX_LENGTH = 128
NUM_RETURN_SEQUENCE = 1
@bentoml.service(
resources={"gpu": 1, "memory": "4Gi"}
)
class GPT2:
model_path = bentoml.models.HuggingFaceModel("openai-community/gpt2")
def __init__(self):
self.generation_pipeline_1 = transformers.pipeline(
task="text-generation",
model=self.model_path,
)
@bentoml.api
def generate(self, sentence: str) -> t.List[t.Any]:
return self.generation_pipeline_1(sentence)
@bentoml.service(
resources={"gpu": 1, "memory": "4Gi"}
)
class DistilGPT2:
model_path = bentoml.models.HuggingFaceModel("distilbert/distilgpt2")
def __init__(self):
self.generation_pipeline_2 = transformers.pipeline(
task="text-generation",
model=self.model_path,
)
@bentoml.api
def generate(self, sentence: str) -> t.List[t.Any]:
return self.generation_pipeline_2(sentence)
@bentoml.service(
resources={"cpu": "2", "memory": "2Gi"}
)
class BertBaseUncased:
model_path = bentoml.models.HuggingFaceModel("google-bert/bert-base-uncased")
def __init__(self):
self.classification_pipeline = transformers.pipeline(
task="text-classification",
model=self.model_path,
tokenizer=self.model_path,
)
@bentoml.api
def classify_generated_texts(self, sentence: str) -> float | str:
score = self.classification_pipeline(sentence)[0]["score"] # type: ignore
return score
@bentoml.service(
resources={"cpu": "4", "memory": "8Gi"}
)
class InferenceGraph:
gpt2_generator = bentoml.depends(GPT2)
distilgpt2_generator = bentoml.depends(DistilGPT2)
bert_classifier = bentoml.depends(BertBaseUncased)
@bentoml.api
async def generate_score(
self, original_sentence: str = "I have an idea!"
) -> t.List[t.Dict[str, t.Any]]:
generated_sentences = [ # type: ignore
result[0]["generated_text"]
for result in await asyncio.gather( # type: ignore
self.gpt2_generator.to_async.generate( # type: ignore
original_sentence,
max_length=MAX_LENGTH,
num_return_sequences=NUM_RETURN_SEQUENCE,
),
self.distilgpt2_generator.to_async.generate( # type: ignore
original_sentence,
max_length=MAX_LENGTH,
num_return_sequences=NUM_RETURN_SEQUENCE,
),
)
]
results = []
for sentence in generated_sentences: # type: ignore
score = await self.bert_classifier.to_async.classify_generated_texts(
sentence
) # type: ignore
results.append(
{
"generated": sentence,
"score": score,
}
)
return results
此示例创建一个工作流,该工作流:
接受文本提示作为输入
并行使用 GPT2 和 DistilGPT2 生成新文本
顺序使用 BERT 对每个生成的文本响应进行评分
返回生成的文本及其得分
注意
在某些情况下,您可能希望将一个 LLM 的输出直接流式传输到另一个 LLM 作为输入,以构建复合 LLM 系统。目前 BentoML 尚不支持此功能,但已列入其路线图。如果您对此主题感兴趣,欢迎加入我们的 BentoML Slack 社区讨论,或在 GitHub 上提出问题。